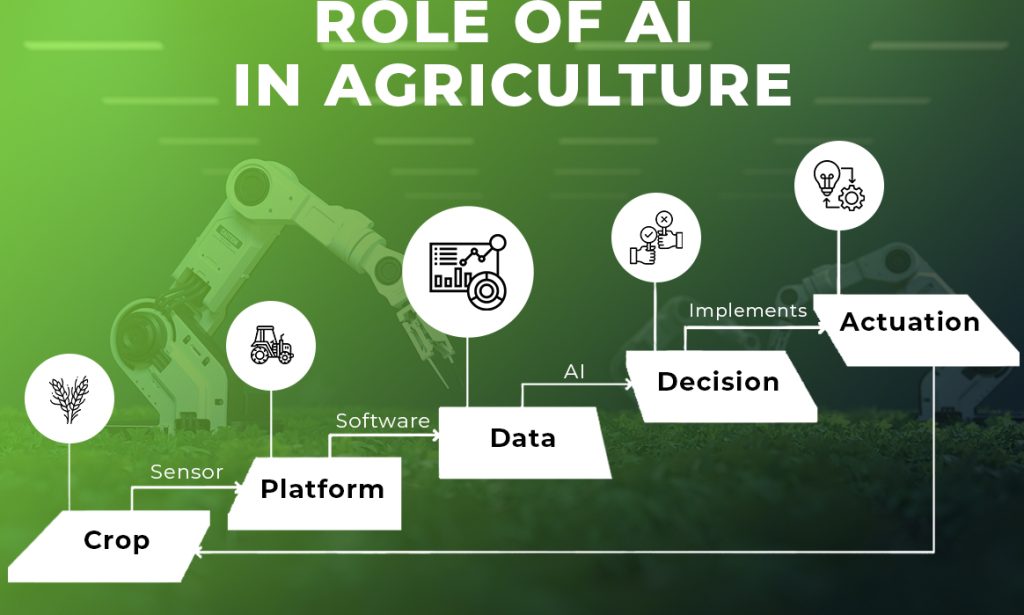
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the agricultural landscape, introducing revolutionary ways to enhance efficiency and productivity in farming. From advanced weather forecasting to precision farming and market analysis, AI technologies are enabling farmers to make informed decisions and optimize their agricultural practices. Here’s a closer look at how AI is reshaping various aspects of agriculture.
Weather Forecasting and Climate Analysis
AI-powered weather forecasting systems use machine learning to analyze meteorological data, satellite imagery, and historical weather patterns. These sophisticated models provide farmers with accurate forecasts of climatic conditions, helping them plan better for planting, irrigation, and pest control. By anticipating weather changes, farmers can safeguard crops against adverse conditions and improve their yield.
Soil Health Monitoring and Nutrient Management
AI-driven technologies are revolutionizing soil health monitoring by utilizing sensors and remote sensing data to assess soil properties accurately. These systems detect nutrient deficiencies, track moisture levels, and identify potential soil-borne diseases, offering recommendations to optimize soil health and crop growth. This targeted approach reduces the reliance on chemical fertilizers and enhances sustainable farming practices.
Precision Farming and Smart Agriculture
Precision farming is one of the most impactful applications of AI in agriculture. Utilizing data from IoT devices, drones, and satellites, AI algorithms provide tailored advice for planting, irrigation, and fertilization. This precise management of agricultural resources not only boosts crop yields but also minimizes environmental impact, paving the way for more sustainable agricultural practices.
Crop Monitoring and Pest Detection
AI technologies are vital in monitoring crop health and detecting early signs of disease, pests, or nutrient deficiencies. Through computer vision and image analysis, AI systems evaluate crop conditions from aerial images, enabling early intervention. This proactive approach helps farmers maintain crop health, reduce chemical use, and minimize crop losses.
Harvesting and Post-Harvest Management
Robotic harvesters and AI-driven sorting technologies automate the harvesting process, reducing labor costs and improving efficiency. These systems can identify ripe produce, perform precision harvesting, and sort outputs by quality criteria. AI also optimizes post-harvest handling by predicting the best storage conditions and managing supply chains effectively, thereby reducing waste and enhancing product quality.
Market Analysis and Decision Support
AI tools integrate various data sources to provide comprehensive market analyses. These insights help farmers understand market trends, consumer demands, and optimal selling times. By employing AI for decision support, farmers can strategically plan crop production and marketing, enhancing their profitability and market adaptability.
Integrated Pest Management
AI facilitates a more integrated approach to pest management by combining data from various sources to predict and mitigate pest outbreaks. This approach not only reduces the environmental impact of pesticides but also increases the efficacy of pest control measures, ensuring healthier crops and higher yields.
Resource and Energy Efficiency
AI contributes significantly to resource management in agriculture, optimizing the use of water, fertilizers, and energy. Smart irrigation systems and energy-efficient practices reduce the consumption of vital resources, lowering costs and supporting environmental sustainability.
Genetic Crop Improvement
AI is playing a crucial role in genetic crop improvement by analyzing genetic data to develop crop varieties that are more resilient to diseases and climatic changes. This genetic optimization helps in producing high-yield, disease-resistant crops that are better suited to specific environmental conditions.
Compliance and Regulation Management
AI systems help farmers navigate the complex landscape of agricultural regulations by providing updated information on compliance requirements. This assists in ensuring that farming practices meet all legal standards, reducing the risk of penalties and enhancing the reputation of agricultural businesses.
Training and Capacity Building
Lastly, AI-driven platforms offer training and support to farmers, helping them adopt new technologies and improve their agricultural practices. These educational tools are crucial for empowering farmers, especially in regions where access to traditional education and training is limited.
Conclusion
Through these diverse applications, AI is not only addressing the immediate challenges of agriculture but also setting the stage for a future where farming is more efficient, sustainable, and aligned with global food demands.













